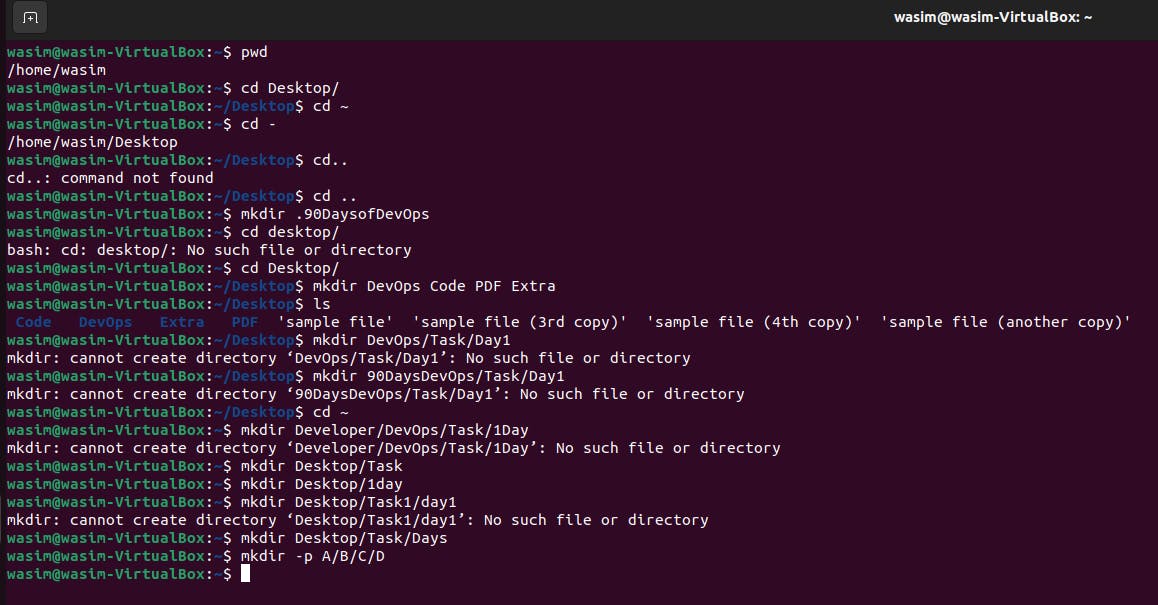
After the Introduction to DevOps, today on our second day we are discussing the very basic linux commands
- This command is used to list files or directories in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems.
ls
- Type this command to list the contents of the directory in a table format with columns including.
ls -l
- Type this command to list files or directories including hidden files or directories. In Linux, anything that begins with a . is considered a hidden file.
ls -a
- Type this command to list all the files having .sh extension.
ls *.sh
- Type this command to list the files and directories with index numbers in inodes.
ls -i
- Type this command to list only directories. (we can also specify a pattern)
ls -d */
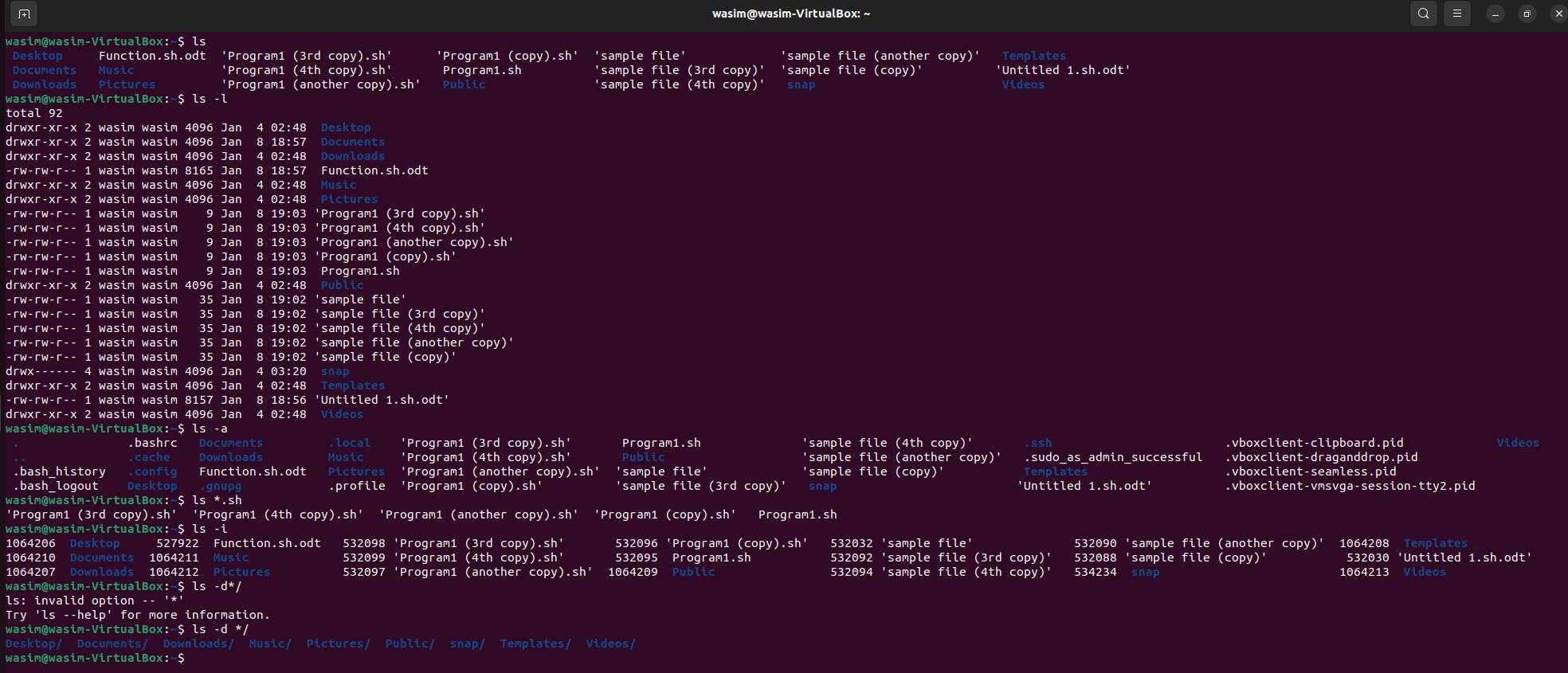
Directory commands
pwd(Print work directory) Use this command to know the present working directory
cd path_to_directoryUse this command to change the directory to the desired path.
cd ~or justcdUse this command to change the directory to the home directory.
cd -Use this command to go to the last working directory.
cd ..Use this command to change the directory to one step back.
cd ../..Use this command for the contents two levels above.
mkdir directoryNameUse this command to make a directory in a specific location
mkdir .NewFolderUse this command to make a hidden directory (also . before a file to make it hidden)
mkdir A B C DUse this command to make multiple directories at the same time.
mkdir /home/user/MydirectoryUse this command to make a new folder in a specific location
mkdir -p A/B/C/DUse this command to make a nested directory.
-pis used to make the parent directoryhistoryUse this command to get all the used command history.
clearUse this command to clear the terminal
rmdir A/B/C/D -pUse this command to delete a directory. Use
-pflag to delete the parent directories as well.touch Myfile.txtUse this command to create a file.
catUse this command to view the content of a file.
--helpUse this command to know more about the command. Example
ls --help.